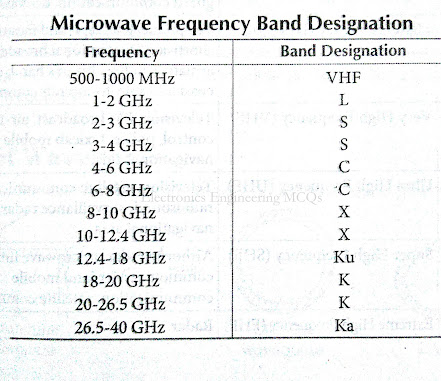
Microwave Frequency Bands
The microwave spectrum is usually defined as a range of frequencies ranging from 1 GHz to over 100 GHz. This range has been divided into a number of frequency bands, each represented by a letter. There are a number of organizations that assign these letter bands. The most common being the IEEE Radar Bands followed by NATO Radio Bands and ITU Bands.
Below you can see tables with details on each letter band.
L Band :
The L Band ranges from 1 to 2 GHz and is used in a number of
applications. Some of the general applications include - Low earth orbit
satellites, military satellites and mobile communications.
S Band :
The S Band ranges from 2 to 4 GHz and is used by a weather and
ship radars and communication satellites. This band is also used for
Earth to space communication, NASA uses this band to communicate with
the International Space Station.
Also Read This: What is S Band?| What is S Band Radar?|Advantages And Disadvantages
C Band :
The C Band is an IEEE Radar Band from 4 to 8 GHz. It contains frequency
ranges that are used for a wide range of applications such as satellite
communication, weather radar systems, WiFi and ISM Band applications.
The C Band is known to perform better than the standard Ku Band (11.2 to
14.5 GHz) for satellite communication in adverse weather conditions.
X Band :
The X Band ranges from 8 to 12 GHz and is used primarily for radar
applications. The short wavelength of the X Band allow for higher
resolution imaging for target identification and discrimination. It is
also used for space communications, portions of this band have been
assigned for deep space communications by the International
Telecommunications Union (ITU). The ITU has also allocated 10 to 10.5
GHz for amateur radio operations and 10.45 to 10.5 GHz for amateur
satellite operations.
Ku Band :
The Ku Band ranges from 12.4 to 18 GHz. The wavelength of the Ku Band is 2.5 to 1.67 cm. this band is used for Satellite Communication.
K Band :
The K Band ranges from 18 to 26.5 GHz. There is part of this band
in the microwave domain and part of it in the infrared domain. The part
in the microwave domain is used for radar and satellite applications
whereas the part in the infrared domain is used for astronomical
observations.
Also Read This: Radio Frequency Band | What is Radio Frequency?

0 Comments
Post a Comment